PROTECT YOUR DNA WITH QUANTUM TECHNOLOGY
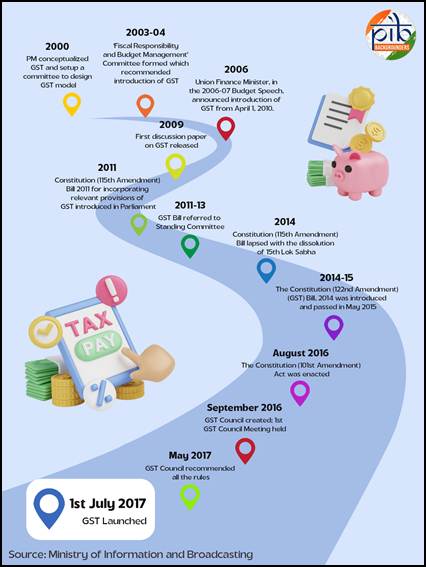
Orgo-Life the new way to the future Advertising by AdpathwayLaunched in a historic midnight session of Parliament in 2017, Goods and Services Tax (GST) has been one of the country's most important economic reforms in the eight years of its existence in 2025. The indirect tax regime, in effect since July 1, 2017, replaces a complex labyrinth of indirect taxes with a simpler, more efficient and unified system, offering a host of advantages, including the creation of a common national market, reduced costs of doing business, and better transparency in the tax system. There has been a consistent rise in the government's revenue collections during this period, with the taxpayer base growing to more than over 1.51 crore active taxpayers.
According to a survey by global professional service network Deloitte, 85 per cent of respondents across industries have had a favourable experience with GST, citing simplified processes, improved credit flow and stronger digital infrastructure.
Stepping into its ninth year, GST continues to evolve with a focus on ease of doing business, improved compliance and wider economic participation.
Here are three key milestones in the eight years of GST:
- Growing GST collections and improving tax compliance: In FY25, gross GST collections hit a record Rs 22.08 lakh crore, marking year-on-year growth of 9.4 per cent and reflecting the growing formalisation of the economy and improved tax compliance.
-
Relief for small businesses: GST has brought much relief to micro, small and medium enterprises (MSMEs) in the form of a higher threshold to this segment. Prior to GST, thresholds under VAT and other state taxes were very low, making compliance difficult for such businesses. The new indirect tax regime also brought a composition scheme, allowing small businesses to pay tax at a fixed rate on their turnover, with minimal paperwork.
-
Boon for logistics players: Transforming the logistics industry, the GST system did away with long queues of trucks at state borders and corruption-prone checkpoints. Goods now move faster and more freely across state lines. The transport time in the country has improved by over 33 per cent, according to several studies. Meanwhile, companies have cut down on fuel costs while major highways are now less congested.
GST structure and salient features
The GST rates are decided by the GST Council, which includes representatives from the state and UT administrations.
The current GST structure comrpises four main rate slabs:
- 5 per cent
- 12 per cent
- 18 per cent
- 28 per cent
Besides, there are three special rates:
- 3 per cent on gold, silver, diamond and jewellery
- 1.5 per cent on cut and polished diamonds
- 0.25 per cent on rough diamonds
A GST compensation cess is levied on products such as tobacco products, aerated drinks and motor vehicles at varying rates. This cess is utilised to compensate states for any revenue loss resulting from the transition to the GST system.


 2 weeks ago
7
2 weeks ago
7










 English (US) ·
English (US) ·  French (CA) ·
French (CA) ·  French (FR) ·
French (FR) ·